nLab exceptional geometry
Context
Exceptional structures
exceptional structures, exceptional isomorphisms
Examples
-
exceptional finite rotation groups:
-
and Kac-Moody groups:
-
exceptional Jordan superalgebra,
Interrelations
Applications
Philosophy
Riemannian geometry
Contents
Idea
The classification of Riemannian manifolds with special holonomy contains two “exceptional” cases: G₂-holonomy in dimension 7, and Spin(7)-holonomy in dimension 8. Their study is the topic of exceptional geometry.
Sometimes more generally, exceptional geometry is understood to study spaces controled by exceptional Lie groups in some way.
Properties
In terms of twisted Cohomotopy
coset space-structures on n-spheres:
| standard: | |
|---|---|
| this Prop. | |
| this Prop. | |
| this Prop. | |
| exceptional: | |
| Spin(7)/G₂ is the 7-sphere | |
| since Spin(6) SU(4) | |
| since Sp(2) is Spin(5) and Sp(1) is SU(2), see Spin(5)/SU(2) is the 7-sphere | |
| G₂/SU(3) is the 6-sphere | |
| Spin(9)/Spin(7) is the 15-sphere |
see also Spin(8)-subgroups and reductions
homotopy fibers of homotopy pullbacks of classifying spaces:
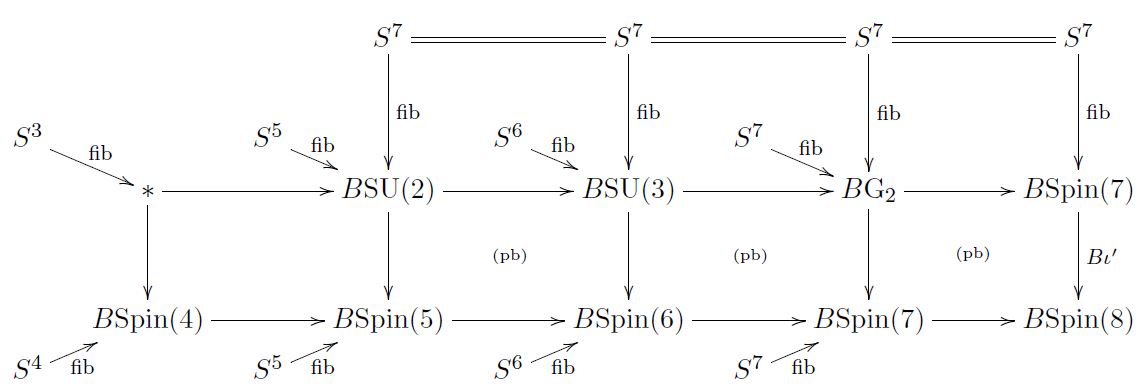
(from FSS 19, 3.4)
Related concepts
References
General
General discussion is in
-
Dominic Joyce, The exceptional holonomy groups and calibrated geometry (pdf)
-
Simon Salamon, A tour of exceptional geometry (pdf)
-
Simon Salamon, Self-duality and exceptional geometry (pdf)
Discussion of G₂ manifolds is in
- Spiro Karigiannis, -manifolds – Exceptional structures in geometry arising from exceptional algebra (pdf)
In supergravity
Applications to U-duality-covariant formulations of 11d supergravity (exceptional field theory, see there for more)
-
George Papadopoulos, Paul Townsend, Compactifications of supergravity on spaces of exceptional holonomy (arXiv:hep-th/9506150)
-
Hermann Nicolai: On M-Theory, J Astrophys Astron 20 (1999) 149–164 [arXiv:hep-th/9801090, doi:10.1007/BF02702349]
-
K. Koepsell, Hermann Nicolai, Henning Samtleben, An exceptional geometry for d=11 supergravity? (arXiv:hep-th/0006034)
-
Christopher M. Hull, Generalised Geometry for M-Theory, JHEP 0707:079 (2007) [arXiv:hep-th/0701203, doi:10.1088/1126-6708/2007/07/079]
For more along these lines see the references at exceptional generalized geometry.
Exceptional-geometric brane sigma-models
On U-duality-covariant exceptional geometric super -brane sigma-models (worldvolume exceptional field theory):
-
Yuho Sakatani, Shozo Uehara, Branes in Extended Spacetime: Brane Worldvolume Theory Based on Duality Symmetry, Phys. Rev. Lett. 117 191601 (2016) [doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.191601, arXiv:1607.04265, talk slides]
-
Yuho Sakatani, Shozo Uehara, Exceptional M-brane sigma models and -symbols, Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics 2018 3 (2018) 033B05, [doi:10.1093/ptep/pty021, arXiv:1712.10316]
-
Domenico Fiorenza, Hisham Sati, Urs Schreiber: Super-exceptional geometry: Super-exceptional embedding construction of M5, J. High Energy Physics 2020 107 (2020) [doi:10.1007/JHEP02(2020)107, arXiv:1908.00042]
-
Domenico Fiorenza, Hisham Sati, Urs Schreiber: Super-exceptional M5-brane model – Emergence of SU(2)-flavor sector, J. Geometry and Physics 170 (2021) 104349 [doi:10.1016/j.geomphys.2021.104349, arXiv:2006.00012]
-
David Osten: Currents, charges and algebras in exceptional generalised geometry, J. High Energ. Phys. 2021 70 (2021) [doi:10.1007/JHEP06(2021)070, arXiv:2103.03267]
-
Machiko Hatsuda, Ondřej Hulík, William D. Linch, Warren D. Siegel, Di Wang, Yu-Ping Wang: -theory: A brane world-volume theory with manifest U-duality, J. High Energ. Phys. 2023 87 (2023) [doi:10.1007/JHEP10(2023)087, arXiv:2307.04934]
-
David Osten: On exceptional QP-manifolds, J. High Energ. Phys. 2024 28 (2024) [doi:10.1007/JHEP01(2024)028, arXiv:2306.11093]
-
David Osten: On the universal exceptional structure of world-volume theories in string and M-theory, Physics Letters B 855 (2024) 138814 [doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2024.138814, arXiv:2402.10269]
-
Machiko Hatsuda, Ondřej Hulík, William D. Linch, Warren D. Siegel, Di Wang, Yu-Ping Wang: Strings and membranes from -theory five brane [arXiv:2410.11197]
Last revised on November 20, 2024 at 17:22:48. See the history of this page for a list of all contributions to it.